
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), positioned at the center of the knee, is a vital connector of bones. These bands of tissue, known as ligaments, ensure the bones remain interconnected. One of the ACL’s main functions is to prevent the shin bone from shifting ahead of the thigh bone.
Injuring the ACL results from an excessive stretch or tear in this ligament, with the tear’s severity ranging from partial to complete.
When the ACL is compromised, it jeopardizes knee stability, leading to reduced leg strength and limited knee mobility.
In cases of severe tears or ruptures, surgical intervention might be necessary. To fully reinstate mobility, a comprehensive rehabilitation journey is often required.1
This article outlines a series of exercises that can significantly contribute to ACL recovery.
Nurturing ACL Rehabilitation at Home
These home-based exercises are instrumental in ACL recuperation. They assist in regaining strength and flexibility while safeguarding the ACL against further harm.
It is pivotal to shun exercises that load or strain the knee. Instead, the emphasis should lie on bolstering the muscles encircling the knee joint.
Among these are the quadriceps (“quads”) that grace the front of the leg and the hamstrings (“hams”) that drape the back of the thigh. Reinforcing these muscle groups gradually restores the range of motion, preventing the knee from immobilization.2
These exercises are ideal for home practice, ideally in consultation with a physician or a physical therapist. They can prepare you for ACL surgery or complement your structured rehabilitation plan.

Commence Your ACL Rehabilitation with these Gentle Exercises
Consider these three effective and safe exercises for early-stage ACL injury rehabilitation. Undertake these exercises cautiously, especially when the knee is still delicate.3
Heel Glides
This exercise focuses on extending the knee without placing any weight on it.
- Begin by sitting on the floor, legs extended.
- Gently flex the injured knee, sliding the heel towards your body.
- Gradually return the foot to the starting position.
- Repeat this sequence ten times.
Isometric Quadriceps Contractions
This seated exercise targets the quadriceps, the muscles along the front of the thigh.
- Sit on the floor with the injured leg extended and the other leg bent.
- Constrict the quadriceps of the injured knee without moving the leg.
- Hold for ten seconds.
- Relax.
- Perform this sequence ten times.
Prone Knee Flexion
Lying on your stomach, engage in this exercise to alleviate knee discomfort.
- Lie on your stomach with your legs straight.
- Flex the injured knee, drawing the heel towards your buttocks.
- Hold for five seconds.
- Relax.
- Repeat this process ten times.
Graduating to More Dynamic ACL Exercises
As swelling diminishes, you’ll gradually find equilibrium in standing on both legs without favoring the uninjured one. Upon achieving this, you can progress to the following exercises.
Passive Knee Extensions
For this exercise, you’ll need two chairs of equal height positioned facing each other. The gap between them should be slightly less than your leg’s length.
- Sit in one chair, placing your heel on the other’s seat.
- Allow your leg to relax, naturally extending the knee.
- Remain in this position for 1 to 2 minutes several times a day. This aids in a gradual hamstring stretch.
Heel Elevations
This standing exercise improves stability.
- Start by gripping the back of a chair for balance.
- Elevate your heels, standing on your tiptoes.
- Maintain this stance for 5 to 10 seconds.
- Gradually lower your heels.
- Perform this cycle ten times.
Partial Squats
Standing with support, engage in this exercise.
- Keep your feet shoulder-width apart.
- Gently bend your knees and lower your hips into a partial squat.
- Sustain this pose for ten seconds before returning to a standing posture.
- Repeat this sequence ten times.
Knee Flexion
Employ a TheraBand or an exercise band for this exercise.
- Attach one end of the band to a sturdy table leg and the other around your injured ankle.
- Facing the table, slowly bend the knee around 45 degrees, against the band’s resistance.
- Hold for a few seconds before resuming the standing position.
- Repeat this process ten times.
Single Leg Balance
This exercise evaluates and reinforces strength and equilibrium.
- Begin by standing on both feet.
- Lift the uninjured leg and stand unaided on the injured leg for ten seconds.
- Initially challenging, this exercise improves with practice, nurturing your strength and stability.
Summing Up Your ACL Journey
An ACL injury results from excessive stretching or tearing of the knee’s ACL ligament. Recovery from such an injury might necessitate surgery or an extensive rehabilitation process.
Home exercises serve as a supportive measure while awaiting surgery or embarking on rehabilitation. Initiating with gentle exercises, and avoiding knee compression and strain, forms the cornerstone of this process.
As swelling subsides, progressing to standing exercises on both legs fosters dynamic rehabilitation.
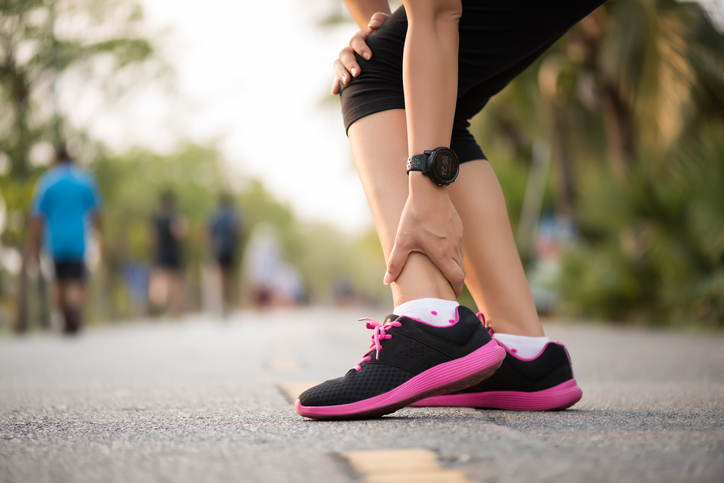

Sprains, strains, and ankle pains are common injuries that can significantly impact mobility and daily activities. Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the rehabilitation and recovery process for these conditions. In this informative blog, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for sprains, strains, and ankle pains, highlighting the important role of physical therapy in restoring strength, mobility, and overall functionality.
Understanding Sprains, Strains, and Ankle Pains
Sprains and strains are common injuries that affect the ligaments and muscles respectively, while ankle pains encompass a range of conditions affecting the ankle joint. These injuries can occur due to sudden twisting, overexertion, repetitive motions, or accidents. Common symptoms include pain, swelling, bruising, limited range of motion, and difficulty bearing weight.
Diagnosis and Evaluation
To accurately diagnose sprains, strains, and ankle pains, a physical therapist will conduct a thorough examination, review the medical history, and may order diagnostic tests such as X-rays or MRIs. This helps determine the severity and extent of the injury, guiding the treatment plan.
The Role of Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the comprehensive treatment and rehabilitation of sprains, strains, and ankle pains. The physical therapist will work closely with the patient to develop an individualized treatment plan focused on reducing pain, restoring range of motion, and improving strength and stability.
Rehabilitation Techniques and Therapeutic Exercises
The initial treatment for sprains, strains, and ankle pains often involves the R.I.C.E. method: Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. As the healing process progresses, physical therapists employ various techniques and therapeutic exercises. Manual therapy techniques, including soft tissue massage and joint mobilization, help reduce pain and improve range of motion. Strengthening exercises target the affected muscles and surrounding areas to restore stability and function. Balance and proprioception training are vital for improving coordination and preventing future injuries. Gait and functional training focus on regaining normal walking patterns and preparing the patient for a return to daily activities.

Modalities and Assistive Devices
Physical therapists may utilize modalities and assistive devices to enhance the healing process. Heat and cold therapy provide pain relief and aid in reducing inflammation. Electrical stimulation can be used for muscle activation and pain management. Ultrasound therapy promotes tissue healing and decreases inflammation. In some cases, bracing, taping, or orthotic devices may be recommended to provide additional support and protection during the recovery phase.
Progress Monitoring and Adjustments
Throughout the treatment process, physical therapists regularly monitor progress and make necessary adjustments to the treatment plan. They track improvements in pain levels, range of motion, and strength. Based on the patient’s progress and any setbacks encountered, modifications to the treatment plan are made to ensure optimal outcomes.
Injury Prevention and Education
Physical therapists play a vital role in educating patients on injury prevention strategies. They provide guidance on proper body mechanics, warm-up exercises, and stretching routines. Patients are empowered with knowledge about self-care and home exercises to maintain their progress and prevent future injuries.
Return to Activity and Performance
Physical therapists guide patients through a gradual and guided return to sports or physical activities. Functional training focuses on ensuring safe and efficient movement patterns during these activities. Individualized strategies are developed to help patients maintain long-term health, well-being, and performance.
The Importance of Compliance and Follow-up
To achieve optimal results, it is essential for patients to adhere to the recommended treatment plan and attend follow-up appointments. Open communication with the physical therapist is encouraged to address any concerns or questions that may arise during the recovery process.
Conclusion
Sprains, strains, and ankle pains can be disruptive and challenging, but with the help of physical therapy, recovery is possible. Through a combination of therapeutic exercises, modalities, and education, physical therapists play a vital role in relieving pain, restoring function, and preventing future injuries. If you have experienced a sprain, strain, or ankle pain, consult with a physical therapist who can provide a personalized treatment plan to guide you on the path to recovery and help you regain your strength, mobility, and active lifestyle. Remember, taking the necessary steps toward healing is a journey worth pursuing with the guidance and support of a skilled physical therapy professional.
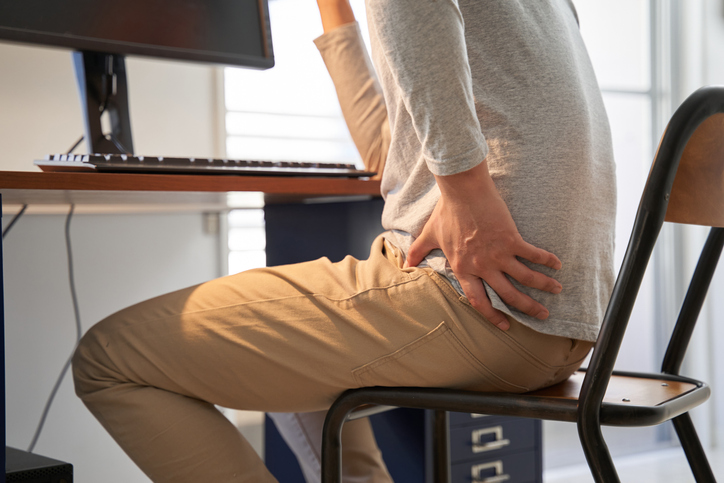
Living with hip and knee pain can be incredibly challenging, impacting one’s ability to perform everyday tasks and diminishing the overall quality of life. However, with the advent of physical therapy, there is hope for effective pain management and relief. In this blog, we will explore how physical therapy can alleviate hip and knee pain, allowing individuals to regain their mobility and independence.
Understanding Hip and Knee Pain
a. Causes of Hip Pain
Hip pain can arise from various conditions, including osteoarthritis, bursitis, hip impingement, and muscle strains or tears. Understanding the underlying cause is essential for effective treatment.
b. Causes of Knee Pain
Knee pain commonly stems from factors such as osteoarthritis, ligament injuries (ACL, MCL), meniscus tears, and patellofemoral pain syndrome. Identifying the root cause helps in tailoring appropriate interventions.
The Role of Physical Therapy in Pain Management
a. Comprehensive Assessment
Physical therapists conduct a thorough assessment, including reviewing medical history, performing a physical examination, and assessing functional limitations. This information guides the development of an individualized treatment plan.
b. Individualized Treatment Plan
Physical therapists create customized treatment plans based on the assessment results. These plans may include pain relief modalities like ice or heat therapy, manual therapy techniques, targeted strengthening exercises, and stretching and flexibility exercises.

Benefits of Physical Therapy for Hip and Knee Pain Relief
a. Pain Reduction
Physical therapy offers targeted pain management strategies that alleviate discomfort without relying solely on medication. Through joint mobilization techniques and other interventions, physical therapists help patients find relief from hip and knee pain.
b. Improved Mobility and Function
Strengthening weak muscles and restoring joint range of motion are central to physical therapy. By targeting specific muscle groups and implementing exercises and techniques, physical therapists help patients regain mobility and improve overall function.
c. Avoidance of Surgery
In some cases, physical therapy can serve as a viable alternative to surgery. Physical therapists may engage in prehabilitation, optimizing the patient’s physical condition before surgery to enhance postoperative outcomes. For certain conditions, conservative management through physical therapy may eliminate the need for surgery altogether.
d. Long-term Rehabilitation
Physical therapy is not just about immediate pain relief; it also focuses on long-term rehabilitation. Through exercise routines tailored to the individual’s needs, physical therapists help patients maintain strength, flexibility, and joint health, preventing future injuries and promoting overall well-being.
Techniques and Interventions Used in Physical Therapy
a. Manual Therapy
Physical therapists employ various manual therapy techniques to address hip and knee pain. Joint mobilization involves gentle movements to improve joint function, while soft tissue mobilization and myofascial release target muscles, tendons, and ligaments for pain relief and improved flexibility.
b. Therapeutic Exercises
Targeted therapeutic exercises are crucial components of physical therapy. Strengthening exercises such as squats and lunges help stabilize the hip and knee joints, range of motion exercises improve flexibility, and balance and proprioception exercises enhance stability and coordination.
c. Neuromuscular Reeducation
Physical therapists focus on retraining movement patterns to improve gait, functional movements, and posture. Through gait training and functional exercises, patients can restore normal movement and reduce pain.
d. Modalities
Physical therapists may also employ various modalities to supplement treatment. Heat and cold therapy, electrical stimulation, and ultrasound therapy can provide pain relief, reduce inflammation, and enhance tissue healing.
Role of Physical Therapist in Hip and Knee Pain Management
a. Education and Empowerment
Physical therapists play a vital role in educating patients about their condition and treatment options. They explain the benefits of physical therapy, teach self-management techniques, and guide patients in making lifestyle modifications to support their recovery.
b. Collaborative Care
Physical therapists often work in collaboration with other healthcare professionals to ensure comprehensive care for patients. They communicate and coordinate with orthopedic surgeons, primary care physicians, and other specialists to optimize treatment outcomes.
The Importance of Consistency and Compliance
Maintaining consistency and adhering to the treatment plan provided by the physical therapist is crucial for long-term success. This section will emphasize the importance of following through with exercises, seeking ongoing guidance from the therapist, and integrating therapeutic activities into daily routines.
Conclusion
Physical therapy offers a comprehensive and effective approach to managing hip and knee pain. By addressing the root causes of pain, reducing discomfort, improving mobility and function, and providing long-term rehabilitation, physical therapy empowers individuals to overcome hip and knee pain and regain control over their lives. Consultation with a skilled physical therapist is a crucial step toward a pain-free future, allowing individuals to return to the activities they enjoy and experience an improved quality of life.

Golf is a sport that lasts your entire life and involves repetitive movements that can strain your body. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned player, spending long hours on the golf course or driving range can lead to injuries. To prevent common shoulder and knee injuries, as well as conditions like low back pain and golfer’s elbow, it’s crucial to prepare your body for the season.
Golf requires a careful balance of mobility and stability in our bodies in order to achieve consistent success while enjoying the sport. If there is any dysfunction in these areas, it is crucial to address it promptly to minimize the risk of injury and ensure a safe return to the game.
Before heading out to the golf course, it is crucial to implement some injury prevention strategies. Physical therapists can be valuable resources in teaching golfers about correct posture and movement mechanics, as well as improving their strength and core control. By doing so, golfers can reduce their risk of injury and stay pain-free while playing the game.
Tips for Playing Golf without Pain
- Warm up before playing: To avoid injuries, it’s crucial to warm up your body before hitting the golf course. Simple stretches and gentle exercises targeting the muscles you use in golf can help prevent pain and strains.
- Use proper posture: Maintaining good posture throughout your swing is essential for preventing pain. Keep your back straight, shoulders relaxed, and knees slightly bent. Avoid hunching over or locking your joints during the swing.
- Strengthen your core: Having a strong core can help stabilize your body and reduce the strain on your back and other muscles. Incorporate exercises like planks and bridges into your fitness routine to strengthen your core.
- Use the right equipment: Make sure your clubs are the correct size and fit your body properly. Ill-fitting clubs can strain your muscles and joints, leading to pain. Also, investing in golf shoes with proper arch support can help alleviate foot and ankle pain.
- Take breaks: Don’t overexert yourself by playing too many rounds back-to-back. Taking regular breaks and giving your body time to rest and recover can prevent overuse injuries and reduce pain.
- Practice good swing mechanics: Learning and practicing proper swing mechanics can reduce the stress on your body. Take lessons from a certified golf instructor to ensure you’re using the correct technique.
- Listen to your body: If you start feeling pain or discomfort during a round of golf, listen to your body and take a break. Pushing through the pain can lead to more serious injuries. Rest, ice, and seek medical attention if necessary.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water before, during, and after your golf game. Dehydration can cause muscle cramps and increase the risk of injury.
- Stay fit and flexible: Incorporate regular exercise and stretching into your routine to maintain overall fitness and flexibility. This can help improve your golf swing and prevent pain.
- Mind your grip: Gripping the club too tightly can strain your hands and arms, leading to pain. Ensure you have a relaxed grip that allows for proper movement during your swing.
Remember, golf should be an enjoyable activity, so don’t let pain get in the way of your game. Follow these tips to play golf pain-free and maximize your performance on the course.
Physical conditioning is crucial for maintaining proper and repeatable swing mechanics in order to reduce the risk of injury. Core strength and flexibility are particularly important in this regard.
Strength training is an effective way to enhance overall fitness. It involves various exercises that specifically target the muscles in the core, back, upper body, and lower body.
Enhancing Flexibility: Engaging in flexibility training can contribute to increasing one’s range of motion and alleviating muscle tension. This may involve performing stretching exercises targeting areas such as the shoulders, hips, and back.
Some of the most effective physical conditioning exercises for golfers involve activating and strengthening the correct muscles without replicating the golf swing. One such exercise is the deadlift, which targets the glutes and promotes more athletic movements initiated from the hips. This technique is crucial for maintaining proper form in every golf stroke, with a hinged hip position and a flat lower back being key components.
Prepare your body for physical activity by starting with a warm-up, such as dynamic stretching or a light jog. This will help to loosen your muscles and prevent injury. After you are done playing, be sure to cool down by engaging in light static stretching to prevent stiffness and maintain flexibility.
Proper technique in golf involves having a relaxed grip on the club, keeping the back straight throughout the swing, and maintaining good posture. It is important to avoid over-gripping the club, as this can lead to injuries in the elbow and wrist. If your body allows, try initiating both the backswing and downswing with your pelvis and hips.
Proper technique in golf involves having a relaxed grip on the club, keeping the back straight throughout the swing, and maintaining good posture. It is important to avoid over-gripping the club, as this can lead to injuries in the elbow and wrist. If your body allows, try initiating both the backswing and downswing with your pelvis and hips.
How Physical Therapy Can Help Golfers
Physical therapy can be a valuable tool for golfers, aiding in injury prevention and enhancing performance. By addressing physical limitations and imbalances, physical therapists can help golfers optimize their swing mechanics and reduce the risk of injury.
One of the key benefits of physical therapy for golfers is injury prevention. Through a comprehensive evaluation, physical therapists can identify any biomechanical issues or movement patterns that may predispose golfers to common golf-related injuries, such as shoulder strains or low back pain. By developing a personalized exercise program, physical therapists can target specific areas of weakness or tightness, helping golfers to maintain proper alignment and stability throughout their swings.
In addition to injury prevention, physical therapy can also improve golf performance. By assessing a golfer’s flexibility, strength, and posture, physical therapists can identify any physical limitations that may be hindering their swing. Through targeted exercises and stretches, physical therapists can help improve range of motion, muscle strength, and balance, all of which are crucial for a successful golf swing. By addressing these physical limitations, golfers can potentially hit the ball further, achieve more accuracy, and reduce the risk of compensatory movements that can lead to injury.
Furthermore, physical therapy can assist golfers in recovering from injuries or surgeries. Whether it’s rehabilitating a shoulder after rotator cuff surgery or addressing back pain from overuse, physical therapists can develop tailored treatment plans to help golfers regain strength, flexibility, and function. By providing manual therapy techniques, therapeutic exercises, and other modalities, physical therapists can help golfers return to their sport safely and efficiently.
Overall, physical therapy plays a significant role in helping golfers optimize their physical performance, reduce the risk of injury, and recover from any injuries or surgeries they may encounter. By addressing physical limitations, biomechanical issues, and imbalances, physical therapists can help golfers improve their swing mechanics and enhance their overall game.
Physical therapists have a crucial role to play in assisting golfers in enhancing their posture, preventing discomfort, and alleviating pain prior to engaging in the sport. There are numerous ways in which a physical therapist can aid golfers, such as:
Physical therapists can evaluate a golfer’s posture and movement by conducting appropriate movement screenings to detect any weaknesses or imbalances that may be affecting their swing. In certain cases, a video recording of the patient’s swing can provide additional insight into their technique. This assessment involves analyzing the golfer’s stance, grip, backswing, downswing, and follow-through in detail. By pinpointing areas that require improvement, the physical therapist can create a customized treatment plan to address these concerns.
Physical therapists can use different methods to correct posture and movement patterns after identifying areas of weakness or imbalance. These methods include exercises to strengthen weak muscles, stretching to improve flexibility, and manual therapy techniques to release tight muscles or joints. By making these corrections, physical therapists can assist golfers in maintaining a more efficient swing and reducing the likelihood of injury.
Create a customized conditioning program: After evaluating any physical limitations or weaknesses, a physical therapist will design a conditioning program to effectively target your specific needs. The program will concentrate on enhancing your flexibility, strength, balance, and endurance.
Create a customized conditioning program: After evaluating any physical limitations or weaknesses, a physical therapist will design a conditioning program to effectively target your specific needs. The program will concentrate on enhancing your flexibility, strength, balance, and endurance.
The professionals at Greendale Physical Therapy have the skills to assess how you move and find any weak or imbalanced areas that could make you more prone to injuries. Take the first step towards better health on the golf course by scheduling a consultation today.

Sciatica pain is a common condition characterized by a sharp, shooting pain that radiates along the sciatic nerve, which runs from the lower back down through the buttocks and into the legs. It can significantly impair one’s quality of life, making everyday activities challenging and uncomfortable. Fortunately, there are several effective solutions available to alleviate sciatica pain and promote healing. In this blog, we will explore the common causes of sciatica, the benefits of physical therapy, and lifestyle and home remedies that can help manage and prevent sciatica pain.
Sciatica pain is often caused by compression or irritation of the sciatic nerve. Some of the most common causes include:
- Herniated Disc: When a disc in the spine bulges or ruptures, it can put pressure on the nearby nerves, including the sciatic nerve, leading to pain and discomfort.
- Spinal Stenosis: This condition occurs when the spinal canal narrows, causing the nerves to become compressed. Spinal stenosis commonly affects older adults and can result in sciatica symptoms.
- Piriformis Syndrome: The piriformis muscle, located in the buttocks, can become tight or spasmodic, leading to sciatic nerve compression. This condition is often caused by muscle imbalances or overuse.
- Spondylolisthesis: When a vertebra slips forward and puts pressure on the nerves, it can result in sciatica pain. Spondylolisthesis can be caused by age-related wear and tear, trauma, or certain medical conditions.
Physical Therapy for Sciatica Pain Relief
Physical therapy is an essential component of treating sciatica pain, as it focuses on restoring strength, flexibility, and function to the affected areas. Here are some ways physical therapy can provide relief:
- Exercise Programs: A skilled physical therapist can design an individualized exercise program to alleviate pain and strengthen the muscles that support the spine. This may include stretching, aerobic exercises, and specific exercises targeting the core and lower back muscles.
- Manual Therapy: Hands-on techniques such as massage, joint mobilization, and spinal manipulation can help reduce pain, improve mobility, and release tension in the muscles.
- Posture and Body Mechanics: Learning proper posture and body mechanics can help relieve pressure on the sciatic nerve and reduce the risk of further injury. Physical therapists can teach patients how to maintain a neutral spine and provide guidance on ergonomics at home and work.
- Education and Prevention: Physical therapists educate patients about their condition, helping them understand the causes of sciatica and providing strategies for preventing future episodes. This may include guidance on weight management, correct lifting techniques, and exercises to maintain a healthy spine.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies for Sciatica
In addition to physical therapy, there are several lifestyle and home remedies that can complement treatment and provide relief from sciatica pain. Here are some effective strategies:
- Hot and Cold Therapy: Applying a hot or cold pack to the affected area can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. Use a cold pack for the first 48 hours after the onset of pain, followed by hot packs or a warm bath to relax the muscles.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in low-impact exercises such as swimming, walking, or yoga can help strengthen the back and abdominal muscles, promoting proper spinal alignment and reducing the risk of sciatica pain.
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Excess weight can put additional stress on the spine and exacerbate sciatica pain. Adopting a healthy diet and engaging in regular exercise can aid weight management and alleviate pressure on the sciatic nerve.
- Ergonomic Modifications: Making adjustments to your workplace or home environment can help reduce strain on the spine. Ensure that your chair provides proper lumbar support, and use a standing desk or take frequent breaks to avoid prolonged sitting.
- Mind-Body Techniques: Practices such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga can help reduce stress and promote relaxation, which can alleviate muscle tension and reduce sciatica pain.
Conclusion
Sciatica pain can be a debilitating condition that affects numerous individuals. Fortunately, there are effective solutions available to alleviate the symptoms and promote healing. Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the management of sciatica pain, providing targeted exercises, manual therapy, and education to address the root causes. Lifestyle and home remedies complement these efforts, focusing on maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good posture, and implementing self-care strategies. By combining these approaches, individuals suffering from sciatica pain can find relief and regain their quality of life. Always consult with a healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation and personalized treatment plan for your specific condition.








